reading-notes
Domain Modeling
Domain modeling is the process of creating a conceptual model in code for a specific problem. A model describes the various entities, their attributes and behaviors, as well as the constraints that govern the problem domain. An entity that stores data in properties and encapsulates behaviors in methods is commonly referred to as an object-oriented model.
Table in html
A table represents information in a grid format. Examples of tables include financial reports, TV schedules, and sports results.
Basic Table Structure
The <table> element is used
to create a table. The contents
of the table are written out row
by row.
You indicate the start of each
row using the opening <tr> tag.
(The tr stands for table row.)
Each cell of a table is
represented using a <td>
element. (The td stands for
table data.)
At the end of each cell you use a
closing </td> tag
The <th> element is used just
like the <td> element but its
purpose is to represent the
heading for either a column or
a row. (The th stands for table
heading.)
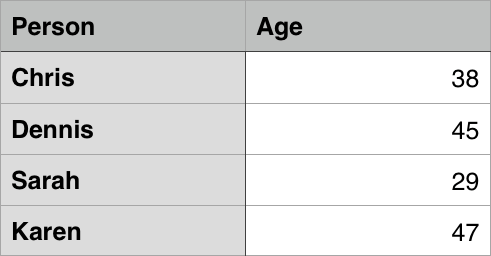
- example of table
Functions is js
Functions are one of the fundamental building blocks in JavaScript. A function in JavaScript is similar to a procedure a set of statements that performs a task or calculates a value, but for a procedure to qualify as a function, it should take some input and return an output where there is some obvious relationship between the input and the output.
- To use a function, you must define it somewhere in the scope from which you wish to call it.
Defining functions
- The name of the function.
- A list of parameters to the function, enclosed in parentheses and separated by commas.
- The JavaScript statements that define the function, enclosed in curly brackets, {…}.
for example
function square(number) {
return number * number;
}
Methods example
const person = {
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe",
id: 5566,
fullName: function () {
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
},
};