reading-notes
HTML Links
- HTML links are hyperlinks.
You can click on a link and jump to another document.
HTML Links - Syntax
The HTML <a> tag defines a hyperlink. It has the following syntax:
<a href="url">link text</a>
The most important attribute of the
<a>
element is the href attribute, which indicates the link's destination. The
link text is the part that will be visible to the reader.
</a>
Email Links
HTML
<a>
tag provides you option to specify an email address to send an email. While
using
<a>
tag as an email tag, you will use mailto: email address along with href
attribute. Following is the syntax of using mailto instead of using http.
example <a href="mailto: abc@example.com">Send Email</a></a
></a
>
HTML Layout Elements
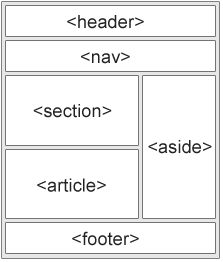
HTML has several semantic elements that define the different parts of a web page:
<header>- Defines a header for a document or a section<nav>- Defines a set of navigation links<section>- Defines a section in a document<article>- Defines an independent, self-contained content<aside>- Defines content aside from the content (like a sidebar)-
<footer>- Defines a footer for a document or a section -
<details>- Defines additional details that the user can open and close on demand <summary>- Defines a heading for the<details>element
HTML Layout Techniques
- CSS framework
- CSS float property
- CSS flexbox
- CSS grid
Functions is js
A function in JavaScript is similar to a procedure a set of statements that performs a task or calculates a value, but for a procedure to qualify as a function, it should take some input and return an output where there is some obvious relationship between the input and the output.
- To use a function, you must define it somewhere in the scope from which you wish to call it.
Defining functions
- The name of the function.
- A list of parameters to the function, enclosed in parentheses and separated by commas.
- The JavaScript statements that define the function, enclosed in curly brackets, {…}.
For example
function square(number) {
return number \* number;
}
Control flow
The control flow is the order in which the computer executes. Code is run in order from the first line in the file to the last line
A typical script in JavaScript or PHP (and the like) includes many control structures, including conditionals, loops and functions. Parts of a script may also be set to execute when events occur.
JavaScript Operators
* let x = 5; // assign the value 5 to x * let y = 2; // assign the value 2 to y
* let z = x + y; // assign the value 7 to z (5 + 2)